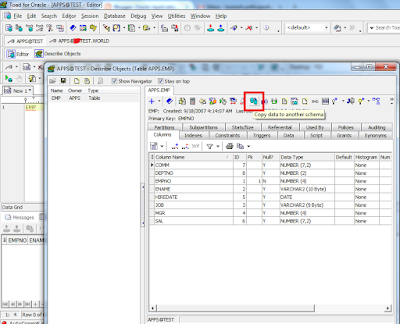
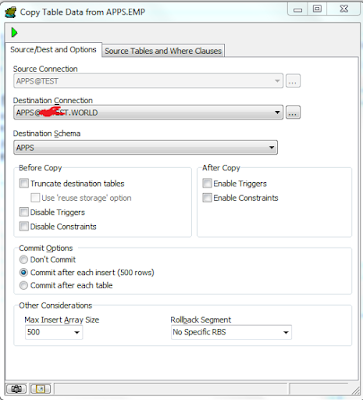
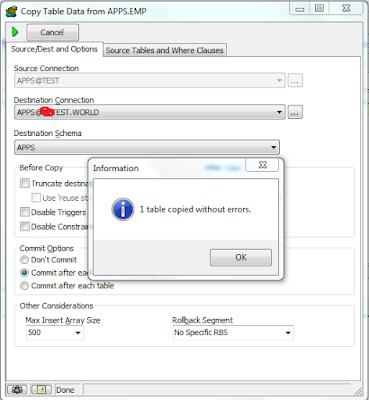
SQL>select dname,sum(sal) from emp,dept where emp.deptno=dept.deptno group by dname;
167) Display itemname and total sales amount for each item.
SQL>select itemname,sum(amount) from item group by itemname;
168) Write a Query To Delete The Repeated Rows from emp table;
SQL>Delete from emp where rowid not in(select min(rowid)from emp group by ename);
169) TO DISPLAY 5 TO 7 ROWS FROM A TABLE
SQL>select ename from emp where rowid in(select rowid from emp where rownum<=7 minus select rowid from empi where rownum<5);
170) DISPLAY TOP N ROWS FROM TABLE?
SQL>SELECT * FROM
(SELECT * FROM EMP ORDER BY ENAME DESC)
WHERE ROWNUM <10;
171) DISPLAY TOP 3 SALARIES FROM EMP;
SQL>SELECT SAL FROM ( SELECT * FROM EMP ORDER BY SAL DESC ) WHERE ROWNUM <4;
172) DISPLAY 9th FROM THE EMP TABLE?
SQL>SELECT ENAME FROM EMP
WHERE ROWID=(SELECT ROWID FROM EMP WHERE ROWNUM<=10
MINUS
SELECT ROWID FROM EMP WHERE ROWNUM <10);
select second max salary from emp;
select max(sal) from emp where sal<(select max(sal) from emp);
173) Delete the 10th record of emp table.
SQL>DELETE FROM EMP WHERE EMPNO=(SELECT EMPNO FROM EMP WHERE ROWNUM<11 MINUS
SELECT EMPNO FROM EMP WHERE ROWNUM<10);